Aluminium Composite Panels (ACP) are a popular choice in modern architecture and design due to their versatility, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Understanding what aluminium composite panels are made of is essential for architects, builders, and designers who want to make informed decisions about materials for their projects. This article will explore the composition, manufacturing process, performance characteristics, applications, and emerging trends in ACPs.
Composition of Aluminium Composite Panels
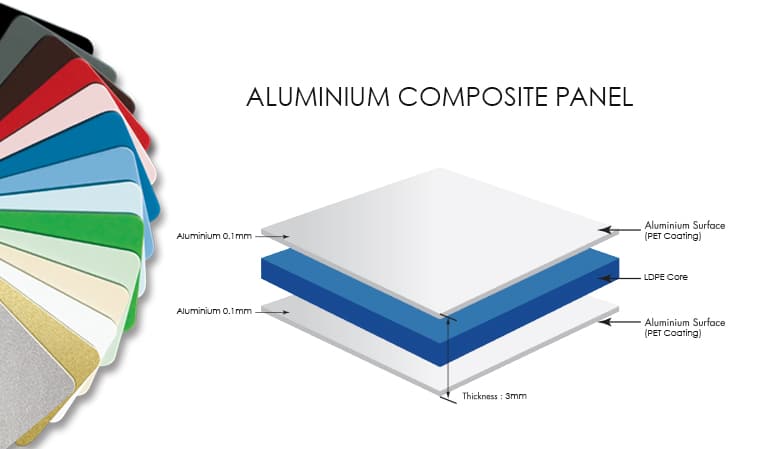
Aluminium composite panels consist of three primary layers: a core layer and two outer aluminium layers. Each component plays a crucial role in the panel’s overall performance and suitability for various applications.
Core Layer
The core layer is the heart of the ACP and can be made from different materials, each offering unique properties:
- Polyethylene (PE) Core
- Most common and cost-effective option.
- Lightweight and easy to fabricate.
- Primarily used in exterior cladding, signage, and architectural applications.
- Lower fire resistance compared to other core materials.
- Mineral-Filled Core
- Contains mineral additives like fire-retardant compounds.
- Significantly improved fire resistance.
- Suitable for high-rise buildings, public spaces, and areas with strict safety regulations.
- Slightly heavier and more expensive than PE cores.
- Fire-Retardant Core
- Special formulation with advanced fire-resistant properties.
- Contains materials like aluminum hydroxide or other non-combustible additives.
- Meets stringent building safety codes.
- Ideal for critical infrastructure and high-risk environments.
Aluminium Outer Layers
The outer layers of an ACP are made from thin sheets of aluminium that provide structural integrity and aesthetic appeal. Key features include:
- Alloy Composition
- Typically uses 3003 or 5005 series aluminium alloys.
- Contains small amounts of manganese or magnesium to enhance strength.
- Thickness ranges from 0.3 to 0.5 mm per layer.
- Offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability.
- Surface Treatments and Coatings
- PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) Coating:Most premium coating option with exceptional UV resistance.
- Polyester Coating:More economical alternative with a good color range.
Additional Coating (Optional)
An optional coating can enhance the performance of the aluminium layers:
- Coating Benefits:
- Provides additional protection against UV radiation and corrosion.
- Maintains color stability over time.
- Enhances the panel’s lifespan and aesthetic appearance.
Manufacturing Process of Aluminium Composite Panels
The manufacturing process of ACP involves several steps that ensure the panels are lightweight, rigid, and versatile.
Continuous Lamination Process
The continuous lamination process is critical for bonding the layers together:
- Involves continuous rolling and bonding of aluminium sheets to the core material.
- Precise temperature and pressure control ensures uniform adhesion and consistent panel quality.
Coating Methods
Coating methods play a significant role in determining the final appearance and durability of ACPs:
- Coil Coating: Applied before panel fabrication to ensure uniform coverage across large surfaces.
- Post-Fabrication Painting: Allows for customization after the panels have been formed, providing various finishes like metallic, matte, glossy, or textured surfaces.
Performance Characteristics of Aluminium Composite Panels
Aluminium composite panels are known for their excellent performance characteristics that make them suitable for various applications:
- Lightweight: Typically weighs between 3-4 kg per square meter, making it easy to handle and install.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Provides structural integrity without adding excessive weight to buildings.
- Excellent Thermal Insulation: Helps maintain energy efficiency in buildings by reducing heat transfer.
- Sound Absorption Properties: Contributes to noise reduction in urban environments.
- Resistance to Weathering: Durable against environmental conditions such as rain, wind, and UV radiation.
Applications of Aluminium Composite Panels
Aluminium composite panels are widely used across various industries due to their versatility. Some common applications include:
- Exterior building facades
- Interior wall cladding
- Signage and advertising boards
- Curtain walls
- Transportation industry (vehicle bodies)
- Industrial equipment casings
- Architectural decorative elements
Environmental Considerations
Aluminium composite panels offer several environmental benefits:
- Recyclable Material: ACPs can be repurposed or melted down for new aluminium products at the end of their lifecycle.
- Sustainable Manufacturing Processes: There is an increasing focus on sustainable practices in the production of ACPs, with some manufacturers offering panels with recycled content.
Potential Limitations of Aluminium Composite Panels
While ACPs have many advantages, there are some limitations to consider:
- Not suitable for load-bearing structural applications due to their lightweight nature.
- Can be damaged by severe impacts; thus, care must be taken during installation and use.
- Requires professional installation to ensure proper handling and adherence to safety standards.
- Performance can vary based on core material quality and coating specifications.
Emerging Trends in Aluminium Composite Panels
The industry is witnessing several emerging trends that enhance the functionality and sustainability of ACPs:
Development of More Fire-Resistant Cores
With increasing safety regulations, manufacturers are focusing on developing cores that offer enhanced fire resistance without compromising on weight or cost.
Advanced Coating Technologies
Innovations in coating technologies are leading to improved durability, aesthetics, and environmental sustainability. This includes coatings that provide self-cleaning properties or enhanced UV protection.
Integration of Smart Technologies
Some manufacturers are exploring the integration of smart technologies into ACPs. This could involve embedding sensors that monitor environmental conditions or structural integrity over time.
Increased Focus on Sustainable Manufacturing
As sustainability becomes a priority across industries, manufacturers are adopting eco-friendly practices in producing ACPs. This includes using recycled materials in production processes or implementing energy-efficient manufacturing techniques.
Selection Considerations for Aluminium Composite Panels
When choosing aluminium composite panels for a project, several factors should be considered:
- Fire Safety Regulations: Ensure compliance with local building codes regarding fire safety standards.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess the environmental impact on the material based on location (e.g., coastal areas may require more corrosion-resistant options).
- Aesthetic Requirements: Choose colors, finishes, and textures that align with design goals while considering maintenance needs over time.
- Budget Constraints: Evaluate cost-effectiveness based on project requirements while balancing quality with affordability.
- Long-Term Performance Expectations: Consider how the selected materials will perform over time under various conditions (e.g., weather exposure).
Conclusion
Understanding what aluminium composite panel is made of is crucial for making informed decisions about their use in construction and design. With a combination of durable aluminium layers and versatile core materials, ACPs offer an array of benefits including lightweight construction, excellent insulation properties, aesthetic flexibility, and environmental sustainability. As technology advances, so too does the potential for innovation within this material category. By considering factors such as application requirements, safety regulations, aesthetic preferences, budget constraints, and long-term performance expectations, architects and builders can effectively leverage aluminium composite panels in their projects.

Leave a Reply